GALEAS Bladder NHS service evaluation
Andy Goffe is Lead Urology Nurse Consultant at Dorset County Hospital Foundation Trust. He leads on the GALEAS ™ Bladder service evaluation and explains how it works. “All patients bring their urine samples into the clinic, or test on arrival. The sample is checked for infection, and we talk to the patient about GALEAS Bladder.”
“The most important message for the patient is that they don’t have to do anything to be part of this. We also explain that we’re looking for ways to replace a cystoscopy, so perhaps it is not a surprise that, to date, 100% of patients have agreed to get involved. It’s a really simple process for both the patient and our team and it takes seconds to upload to the GALEAS Bladder portal. We love embracing new technologies and are very excited about the potential of GALEAS Bladder to transform our service”.
Why choose our GALEAS Bladder service?
Tried and tested
Delivering accuracy for NHS and now being adopted by leading private healthcare providers.
Non-invasive test
A simple, non-invasive urine sample test that can be provided from the patient’s home.
One test for all stages
Delivers results equivalent to cystoscopy for all stages of bladder cancer, including both Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) and Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC).
High sensitivity
Delivers >90% sensitivity (higher in some grades, see table 2 below) allowing clinicians to make informed decisions about which patients need further investigation.
Sample to report service
We provide an end-to-end service. Sample kits are sent to our UK-based laboratory for testing and our team of HCPC-registered Clinical Scientists review each report prior to release.
Quality assurance
Our team of experts are focused on quality and maintaining the highest standards of work across all services.
Rapid turnaround time
We can deliver results within 10 working days of receiving the sample.
How our service works

Urologist requests a urine collection device for patient

Patient sends barcoded urine sample to service laboratory

Lab uploads sequencing results to secure cloud-based GALEAS platform

Results analyzed, report generated and shared directly with urologist

Urologist shares results with patient and discusses next steps
Bladder Cancer Panel
Our GALEAS Bladder Cancer service is based on a genetic biomarker test comprised of 23 of the most relevant bladder cancer associated genes.
The somatic mutations covered by the kit have been shown to detect 96% of bladder cancers in over 770 clinical samples 1, 2
Table 1. Gene list included in the GALEAS Bladder cancer test
| AKT1 | ERBB2 | NRAS |
| BRAF | ERBB3 | PIKC3A |
| C3orf70 | ERCC2 | RHOB |
| CDKN1A | FBXW7 | RXRA |
| CDKN2A | FGFR3 | SF3B1 |
| CREBPP | HRAS | TERT (promoter) |
| CTNNB1 | KDM6A | TP53 |
| ELF3 | KRAS |

How are samples sequenced?
Our GALEAS Bladder service is delivered through our Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) pipeline.
We use Cell3 Target enrichment technology and Illumina sequencing to generate high-quality sequencing data to a read depth of 5M per sample, using 2 × 150 bp cycling parameters.
To ensure high confidence in the results, key performance parameters have been determined through extensive validation of the Cell3 Target chemistry.
Technical performance
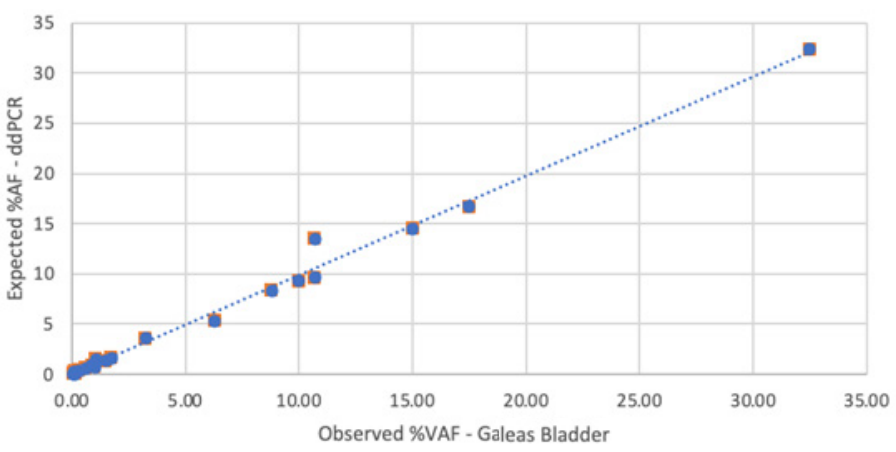
Performance of GALEAS Bladder was assessed in a cohort of reference samples containing mutations across the spectrum of the GALEAS Bladder panel.
GALEAS Bladder shows high sensitivity, detecting over 95% of variants with a variant allele frequency (VAF) greater than 0.1%. 4
Clinical validation
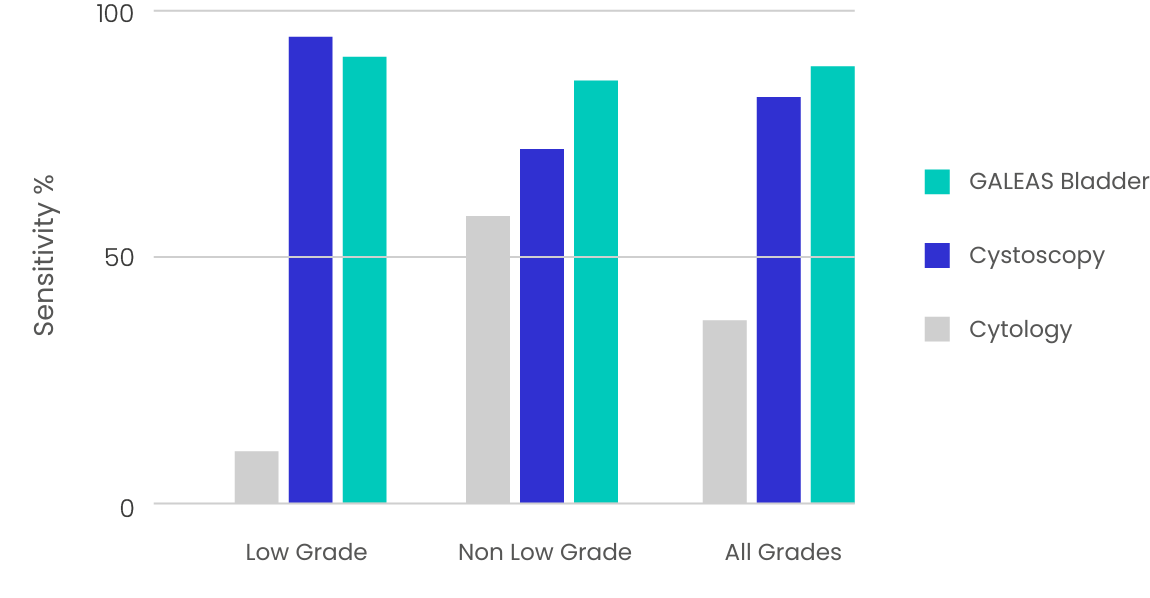
GALEAS Bladder test performance was assessed on 664 urine samples from three UK clinical cohorts, showing high detection sensitivity and specificity across all stages and grades of bladder cancer. 2,3
| - | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| pTa | 86% | 86% |
| T1 | 95% | 86% |
| T2+ | 89% | 86% |
| G1 | 76% | 86% |
| G2 | 92% | 86% |
| G3 | 92% | 86% |
| NMIBC | 89% | 86% |
| MIBC | 89% | 86% |
Table 2. Sensitivity and specificity of GALEAS Bladder across all stages and grades of bladder cancer
References
- Zhu CZ, Ting HN, Ng KH, Ong TA. A review on the accuracy of bladder cancer detection methods. Journal of cancer. 2019;10(17):4038.
- Ward DG, Baxter L, Ott S, Gordon NS, Wang, J,Piechocki K, et al. Highly sensitive and specific detection of bladder cancer via targeted ultra-deep sequencing of urinary DNA. European urology oncology. 2023 Feb 1;6(1):67-75.
- Ward DG, Gordon NS, Boucher RH, Pirrie SJ, Baxter L, Ott S, et al. Targeted deep sequencing of urothelial bladder cancers and associated urinary DNA: a 23‐gene panel with utility for non‐invasive diagnosis and risk stratification. BJU international. 2019 Sep;124(3):532-44.
- Nonacus. GALEAS™ Bladder Datasheet v1. Accessed September 14, 2023.
Research use
Our genomic panel is comprehensively designed, focusing on mutations found in 96% of bladder cancers. This makes it ideal for translational and clinical research as it requires a simple urine sample.
Bladder Cancer kit components
- The GALEAS Urine Collection Device is provided as part of the service
- It contains a simple cardboard collection device, easy to use (ensuring efficient urine collection and return rates)
- The device flat packs reducing storage and shipping costs
- Minimum 50 ml urine required and can be collected in the comfort of the patient’s home
- The sample is returned to the lab in a 50 ml barcoded Falcon tube containing a proprietary preserver solution, stabilising urine samples for up to 28 days at room temperature (18 to 25°C)
- All collection and postage information are provided with the device
- The collection kit has been validated with our DNA extraction kit and NGS library preparation reagents to ensure optimal performance
- Full traceability – the tube is barcoded
- A magnetic bead-based genomic DNA protocol
- Extracts tumor-derived DNA from urinary cell-pellets
- High throughput automated sample processing
- A simple, clear and concise answer, the GALEAS Bladder report is provided as part of the service and is easy to interpret
- Simple yes/no report indicating the likely presence of bladder cancer
- Lists the somatic variants identified
- Created in .PDF format, or in .JSON format for report customisation, sent directly to the requesting clinician