Results in under three hours
Fast turnaround time taking under three hours from sample receipt to result as; cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) extraction is not required and there is a straightforward qPCR protocol.
Less material required
Using less than <0.25 ml of plasma sample, this test leaves plenty of sample for other prenatal tests.
Flexible and fully validated
A validated kit and flexible tube format enables laboratory processing on any qPCR machine.
Multi-target assay
A multi-target approach delivers an assay suitable for all populations and intra-assay concordance for increased sensitivity.
Non-invasive fetal Rhesus D (RhD) blood group testing
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) of cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) in maternal blood during pregnancy can be used to determine fetal Rhesus D blood group status. This means that RhD negative pregnant women can avoid receiving antenatal anti-D immunoglobulin if they are carrying a RhD negative baby and are not at risk of Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFN).
Current practice is to provide antenatal anti-D prophylaxis at 28-30 weeks gestation, which means that about 40% of healthy RhD-negative pregnant women are exposed to a pooled human blood product that they do not need as their baby is also RhD negative.1
The Cell3 Direct: Fetal RhD Blood Group Genotyping kit predicts fetal RhD status with high accuracy, not only improving care for RhD-negative women, but allows health services to apply a targeted approach to anti-D prophylaxis and conserve the use of an expensive product that can be in short supply.
A 'direct from plasma' option for fetal RhD testing
Nonacus have developed the first commercially available, direct from plasma, non-invasive prenatal diagnosis (NIPD) kit for fetal RhD genotyping.
With no cffDNA extraction required and a simple real-time qPCR protocol, the Cell3 Direct: Fetal RhD Blood Group Genotyping kit delivers results direct from plasma in under three hours reducing technician time and providing a quicker, more cost-effective assay than previously available.
If, however, you already have high-throughput processing for extracted cffDNA set up in your laboratory or you are testing at 10-11 weeks when you need to maximize sensitivity, the Cell3 Direct: Fetal RhD Genotyping kit can still be used with extracted cffDNA.

Meets NICE guidelines on fetal Rhesus D status
Non-invasive prenatal testing to identify fetal Rhesus D status is recommended by NICE for pregnant women who are Rhesus D negative as a cost-effective option to guide antenatal prophylaxis with anti-D immunoglobulin (anti-D Ig) within the UK NHS.2
The Cell3 Direct: Fetal RhD Blood Group Genotyping kit meets all of the NICE requirements for this test.
Multi-target approach for a multi-ethnic assay
There are now known to be several genetic causes for an RhD-negative phenotype, and these vary according to ethnic origin. In Caucasians a homozygous deletion of the RhD gene is the predominant cause, but in black Africans the RhD gene is intact but non-functional. This is known as the RhD-pseudogene (RhD-Psi).
It contains a 37 base pair insert in exon 4 and a nonsense mutation in exons 5+6, which may introduce stop codons preventing translation.3 For an assay to be accurate across all populations, it must therefore target multiple exons in the RhD gene.
The Cell3 Direct: Fetal RhD genotyping kit targets sequences specific for exons 5, 7 and 10 of the RhD gene and can distinguish between RhD positive, RhD negative and RhD PSI genotypes making it suitable for any population.

Sensitive qPCR screening for fetal RhD
The technical sensitivity of our assay was demonstrated using RhD positive genomic DNA spiked into an RhD negative background at 10%, and 1% ratios (equivalent to 30 and 3 genomic equivalents) to reproduce realistic fetal fractions.
Amplification of all targets across all replicates was observed even at the lowest 1% spike-in fraction, with RhD exon 5 assay capable of discriminating the RhD PSI variant.
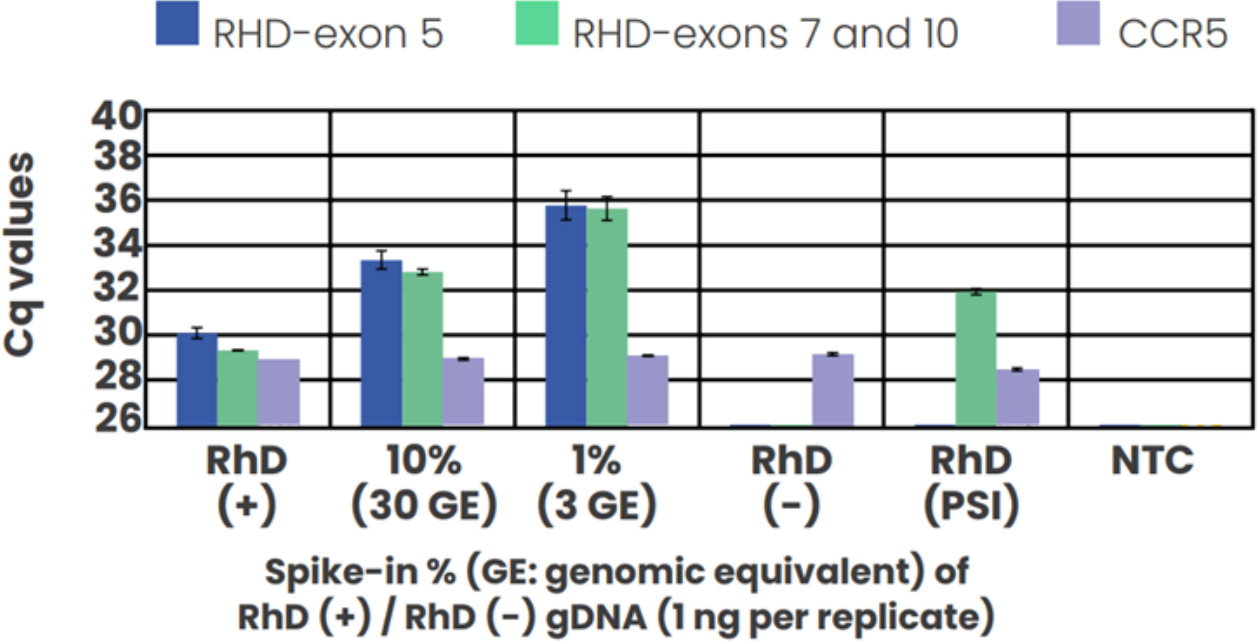
Figure 1: Assay sensitivity and specificity test with spike-in genomic DNA samples
Direct from plasma vs extracted cffDNA
Our direct-from-plasma protocol was compared with extracted cfDNA and results were demonstrated to be comparable using the same plasma sample (RhD positive, 24 weeks gestation).
Amplification plots of direct-from-plasma testing shows robust amplification of all targets: RhD exon 5 (blue), RhD exons 7 and 10 (green) and CCR5 (black).
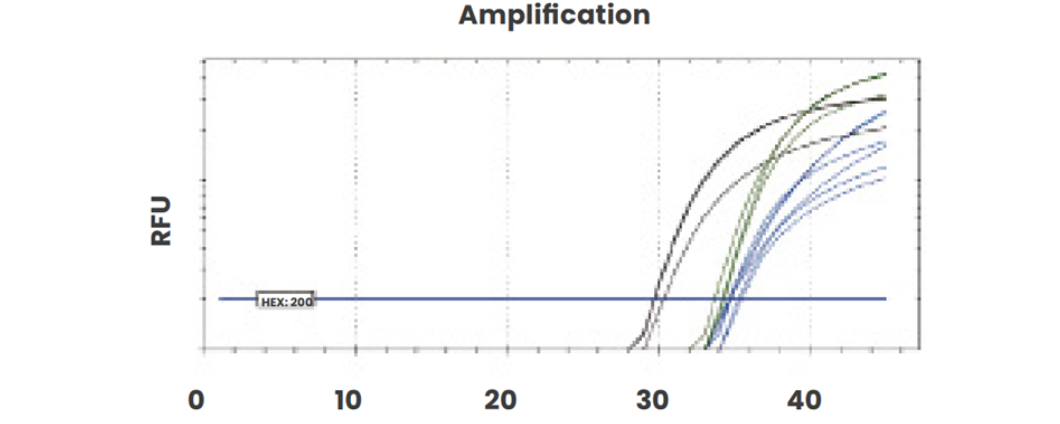
Figure 1a: Extracted cfDNA amplification.
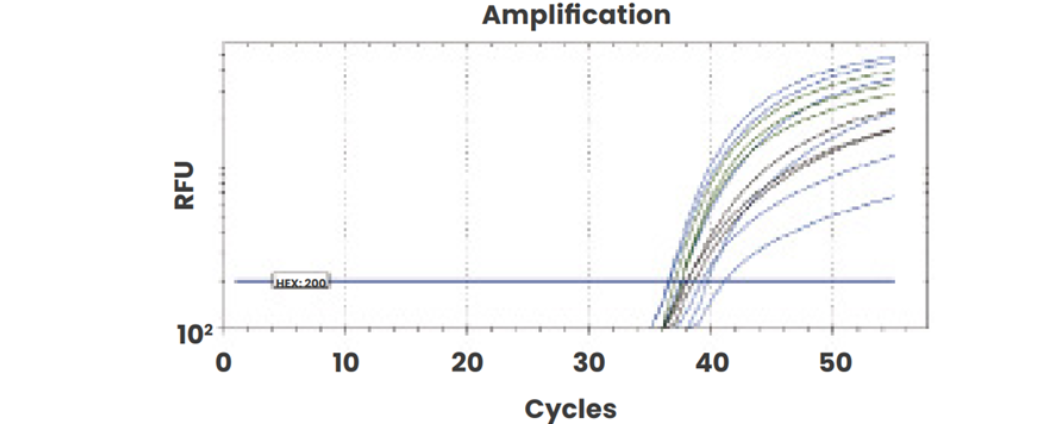
Figure 2b: Direct from plasma amplification.
References
1.Chitty LS, Finning K, Wade A, Soothill P, Martin B, Oxenford K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of routine antenatal determination of fetal RHD status across gestation: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2014;349. Full article.
2. Parks, M. A direct from plasma approach to non-Invasive prenatal fetal sex determination and RhesusD genotyping by quantitative PCR. European Journal of Human Genetics. 2018;26:635-636. Full article.
3. Singleton BK, Green CA, Avent ND, Martin PG, Smart E, Daka A, et al. The presence of an RHD pseudogene containing a 37 base pair duplication and a nonsense mutation in Africans with the Rh D-negative blood group phenotype. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology. 2000;95(1):12-8. Full article
See our customer publications
| Product | Catalog No. |
| Cell3™ Direct: Fetal RhD Genotyping kit, tube format – 96 reaction kit | PCR_RHD_GEN_96 |
